The motor performance curve is a diagram that describes the changes in key parameters of the motor under different loads, and is used to visualize the output characteristics, efficiency and working range of the motor. However, many technical engineers often encounter the following problems when looking at motor curve diagrams:
The type of curve is unclear
Lack of key parameter annotation
The unit is confused or not marked
The voltage conditions are unclear
Lack of temperature or environmental working conditions
The curve data is inconsistent with the actual prototype
The allowable scope of work is not given
Only static graphs are provided, and dynamic response is lacking
To address the above issues, you need to understand the following core elements:
1、Horizontal axis (X-axis): usually torque (unit: Nm or Kg-cm), from left to right indicates a gradual increase in torque
2、Vertical axis (Y-axis): contains four parameters, corresponding to four curves:
Speed shaft (in rpm): The speed decreases with the increase of torque.
Power Shaft (in W): Change in output power.
Efficiency axis (unit: %): The efficiency at which electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy.
Current axis (unit: A): The increase or decrease of the input current.
In the motor curve drawing, the torque-speed curve (TN curve) is the core parameter, and its importance is reflected in the load response core and the basis for judging the adaptation of working conditions
The efficiency curve can best reflect the energy-saving potential of motors, especially for long-term operating systems such as new energy vehicles and industrial equipment
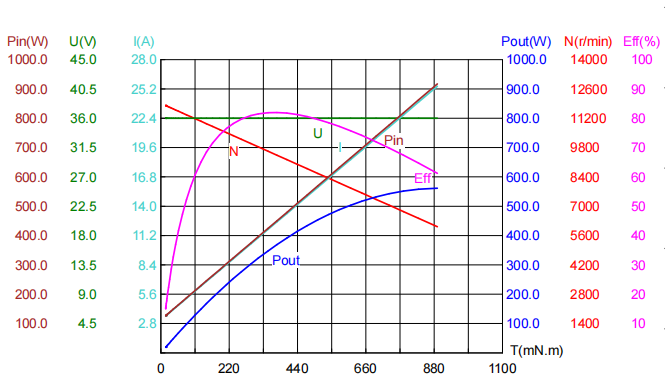
Key Extreme Points :
Maximum efficiency point: 82.0% (corresponding torque 373.6mN·m, rotational speed 9441r/min)
Maximum output power : 561.73W (torque 890.2mN·m, speed 6026r/min)
Stopping Current: 25.461A (Ultimate Torque 890.2mN·m)

1. No load condition (No_Load)
Parameter characteristics: torque 16.2mN·m, speed 11804r/min, efficiency only 15.7%
Adaptive scenarios:
The device starts instantly
Light load operation status (such as low fan gear)
Precautions: The electricity is seriously wasted and should not be operated for a long time
2. Optimal efficiency point (Max_Eff)
Parameter characteristics: torque 373.6mN·m, speed 9441r/min, efficiency 82.0%
Adaptive scenarios:
New energy vehicle drive motor cruise phase
Continuous operation of industrial equipment (energy-saving priority scenario)
Advantages: 0.82W of mechanical energy can be output per 1W of electrical input
3. Maximum power point (Max_Pout).
Parameter characteristics: torque 890.2mN·m, speed 6026r/min, power 561.73W
Adaptation scenario:
Short-term overload of construction machinery (such as the moment of lifting the crane)
Power tools drill holes with high loads
Risk warning: The efficiency is reduced to 61.2%, and the heat dissipation design is required
4. Blocking and turning conditions (Max_Torque).
Parameter characteristics: torque 890.2mN·m, speed 0r/min, current 25.461A
Adaptation scenario:
Servo system position hold
Safety braking device
Protection requirements: Overcurrent protection circuit must be configured
 BACK
BACK
Yesterday, the 138th China Import and Export Fair (Canton Fair) was grandly open…
In the golden autumn of October, the fruits are fragrant. On this beautiful mome…
Dear friends, the 138th Canton Fair will be held in Pazhou, Guangzhou on October…
At BG Motor, we firmly believe that the strength of a team can carry dreams furt…
New Breakthrough at Conifer (Silicon Valley Startup)What’s new?Conifer has devel…
The 2025 World Robot Conference (WRC), held in Beijing, brought together top min…