High ambient temperature: The motor itself is installed in a high temperature environment, and the heat is transferred to the brake components, accelerating the insulation aging of the coil, drying of the grease, and annealing of the spring.
Frequent start and stop: In applications requiring high frequency of point movement and rapid start and stop, the brake works frequently, and the friction plate and coil will continue to generate a large amount of heat, resulting in a sharp rise in the overall temperature beyond the design permission range.
Dust/Particulate matter: If wood chips, metal dust, cement dust and other dust enter the brake, it will aggravate the wear of the friction plate and brake surface, and may jam the moving parts.
Oil/chemicals: Oil can make the friction pads slip and lose braking power; chemicals can corrode metal and insulation.
Damp/water: Causes internal corrosion and reduced electrical insulation, causing short circuit.
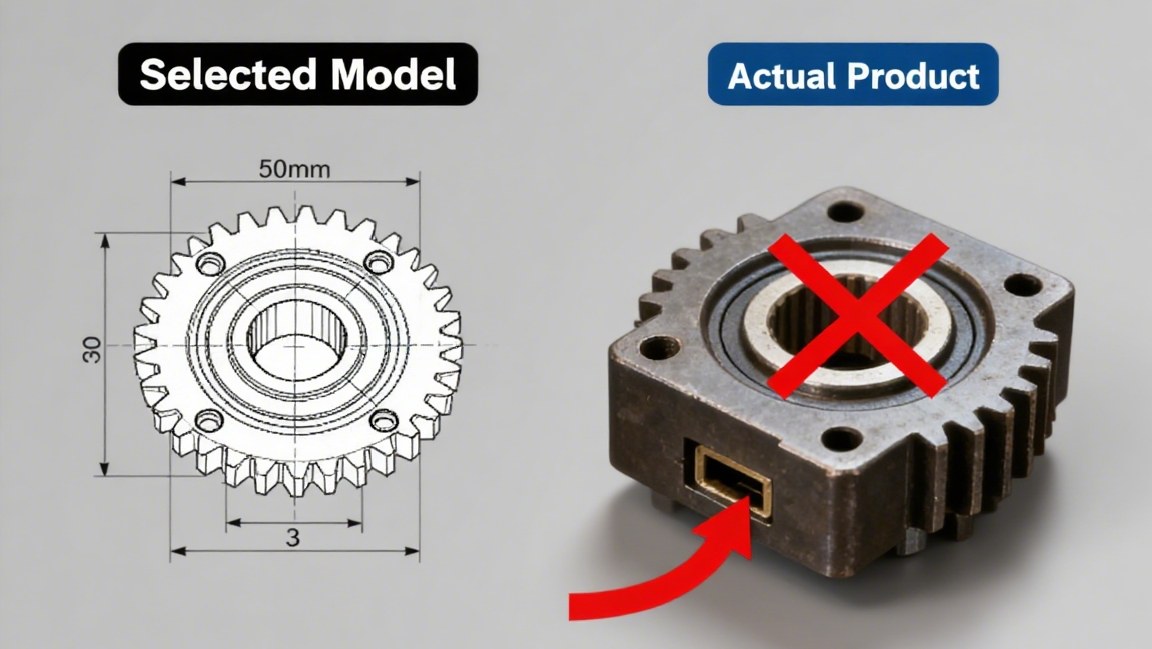
The selected brake torque does not match the load (too small), and it needs to work under overload, which will soon damage.
Overloading: The brake is operated for a long time beyond its rated braking torque.
Using brakes as parking devices: Electromagnetic brakes are designed to hold (prevent shaft rotation) rather than to stop frequently braking high-inertia loads. This use generates significant heat and shock.
When the electromagnetic brake is damaged, you can follow the following ideas to troubleshoot:
Electrical inspection: First, use a multimeter to measure the voltage at both ends of the brake coil, whether it is stable at about 24V when powered on and off. Check whether the wiring is firm and the rectifier diode is normal.
Mechanical inspection: manually check whether the brake arm can move normally and whether there is any jamming. Check the wear degree of the friction pad and the brake clearance.
Environmental assessment: Observe the working environment of the equipment, whether there are high temperature, dust, humidity and other problems.
Review the working condition: confirm whether the recent working frequency and load of the equipment have changed, and whether it exceeds the design capacity of the brake.
In most cases, the damage of electromagnetic brake is not caused by a single reason, but a chain reaction. For example, loose wiring (electrical) leads to coil burnout, and excessive wear of friction pads due to incomplete release (mechanical). Therefore, system troubleshooting is crucial.
 BACK
BACK
Yesterday, the 138th China Import and Export Fair (Canton Fair) was grandly open…
In the golden autumn of October, the fruits are fragrant. On this beautiful mome…
Dear friends, the 138th Canton Fair will be held in Pazhou, Guangzhou on October…
At BG Motor, we firmly believe that the strength of a team can carry dreams furt…
New Breakthrough at Conifer (Silicon Valley Startup)What’s new?Conifer has devel…
The 2025 World Robot Conference (WRC), held in Beijing, brought together top min…